Open Source vs. Closed Source Large Language Models (LLMs): Which is Right for Your Business?
Explore the key differences between open source and closed source large language models (LLMs). Learn which option is best for your business, considering factors like accessibility, customization, cost, and support.
Author
D Team
5 Aug 2024
Introduction:
As artificial intelligence (AI) continues to grow in importance, businesses are increasingly looking to leverage large language models (LLMs) to enhance their operations, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation. When it comes to choosing the right LLM for your business, you’ll likely encounter two primary options: open source and closed source models. But what do these terms mean, and how do they impact your business? This blog will break down the key differences between open source and closed source LLMs, helping you make an informed decision that aligns with your business needs.
What Are Open Source LLMs?
Definition
Open source LLMs are AI models whose source code is publicly available. This means that anyone can use, modify, and distribute the code, making these models accessible to a wide range of users, from individual developers to large organizations.
Advantages of Open Source LLMs
Accessibility: Open source LLMs are freely available for anyone to use. Whether you’re a startup or a large enterprise, you can access these models without the need for expensive licenses, making them an attractive option for businesses looking to experiment with AI.
Customization: One of the biggest strengths of open source LLMs is their flexibility. Since the code is open, you can tailor the model to fit your specific needs. Whether you need a model to understand industry-specific jargon or perform specialized tasks, open source LLMs offer the ability to customize and optimize the model according to your requirements.
Community Contributions: Open source LLMs benefit from a vibrant community of developers and researchers who actively contribute to their improvement. This community-driven approach fosters innovation, as new features, updates, and enhancements are constantly being developed and shared.
Cost-Effectiveness: Since open source LLMs are typically free, they significantly reduce the cost barrier for businesses. This cost-effectiveness allows companies to allocate resources to other areas, such as implementation and scaling, rather than expensive software licenses.
Examples of Open Source LLMs
LLaMA 2: Developed by Meta, LLaMA 2 is available for both research and commercial use, offering flexibility for various applications.
BLOOM: Known for supporting multiple languages, BLOOM is accessible via platforms like Hugging Face, making it a versatile option for global businesses.
BERT: Renowned for its ability to understand context in a bidirectional manner, BERT is widely used in natural language processing tasks.
What Are Closed Source LLMs?
Definition
Closed source LLMs are proprietary models developed and maintained by private organizations. Unlike open source models, their source code is not publicly accessible, meaning that users have limited control over the model’s inner workings.
Advantages of Closed Source LLMs
Dedicated Support: One of the key benefits of closed source LLMs is the professional support that often accompanies them. Businesses can rely on dedicated assistance for troubleshooting, implementation, and optimization, which can be particularly valuable for companies without in-house AI expertise.
Robustness: Closed source LLMs are typically backed by substantial resources, ensuring continuous improvements and updates. This results in highly polished models that are reliable and well-supported, offering peace of mind to businesses that prioritize stability.
Disadvantages of Closed Source LLMs
Limited Control: Because the source code is not accessible, businesses have limited customization options. This can be a drawback if your company needs a model that is specifically tailored to niche or unique requirements.
Cost: Closed source LLMs usually require licenses or subscriptions, which can be costly. For businesses with tight budgets, this might be a significant consideration, especially when compared to the cost-free nature of open source models.
Examples of Closed Source LLMs
GPT-4: Developed by OpenAI, GPT-4 is known for its advanced capabilities and is widely used in a variety of applications, from customer service to content creation.
Gemini: A model developed by Google, Gemini is employed across various applications, offering powerful AI-driven solutions.
Key Differences Between Open Source and Closed Source LLMs
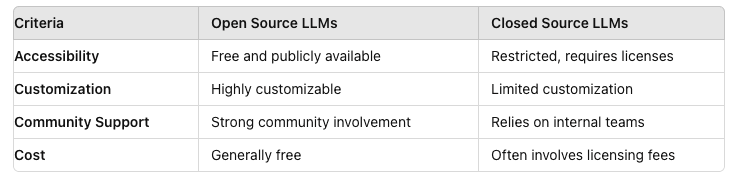
Open source LLMs are ideal for businesses that value flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and community-driven innovation. They provide the freedom to experiment and customize, making them a good fit for companies that have specific needs or are operating on a budget.
Closed source LLMs, on the other hand, offer the assurance of professional support and robust, well-maintained models. These are suitable for businesses that require stability, dedicated assistance, and are willing to invest in high-quality, ready-to-use solutions.
Conclusion
Choosing between open source and closed source LLMs depends on your business’s specific needs, resources, and priorities. If you value customization and cost savings, open source LLMs might be the right choice. However, if you need professional support and a polished product, closed source LLMs could be more suitable. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision, ensuring that your business leverages the full potential of AI.